Architecture of a Continuous Machine Learning System (CMLS) is outlined, The architecture is used as a background for explaining how smart components are stored in a repository, and how they interact with each other when configured as parts of an AI based system or product.
The technology outlined on Ainolabs.com is Patent Pending, USPTO.
Continuous Machine Learning System Architecture
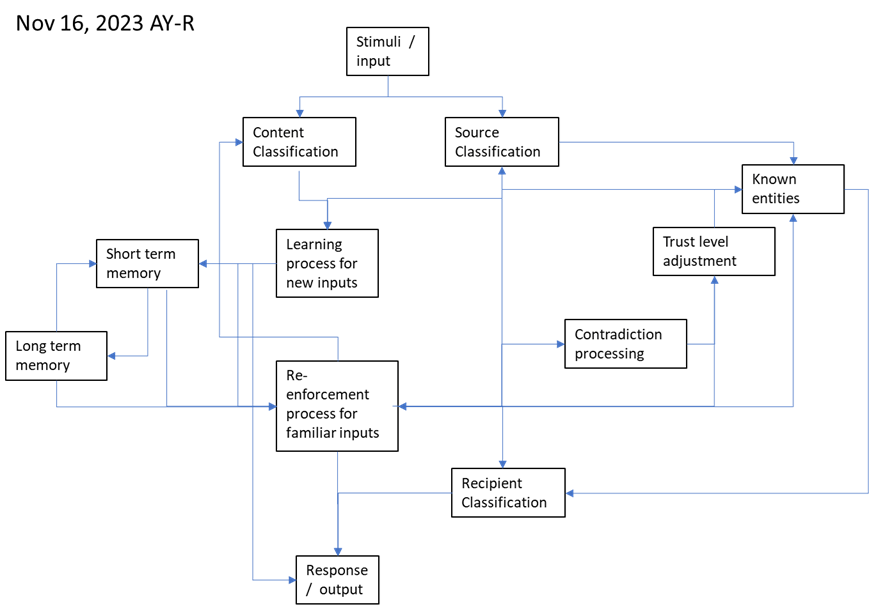
Notes:
– The diagram is a view of ML blocks handling a single stimuli-response –pair.
– Learning is a byproduct of the process. The system may decide to stay silent (no response).
– Source classification – is the input trustworthy?
– Recipient – what can be told to the recipient?
– Learning process – enforcement – short term – long termi memory –handle Continuous Learning and Graceful forgetting.
– Contradiction processing handles cases where the input and memory differ, or consecutive inputs contradict each other (also memory).
– Processing algorithm:
Input I + attributes are passed between blocks.
Each Block contributes to Output O + attributes.
The whole releases O once the Blocks agree (stable response).
O can be empty.
Learning Processes
A closer view of how the Learning Processes operate:

Notes:
-Content classification module recognizes specific input categories.
-This impacts processing. Input is either ”general” (non-spcialized NN or other system),or specific to the input (e.g. ”math software for a math problem”).
-Learning process always impact Short term memory.
-Impacts on Long Term memory (new or re-enforced leaning) depend on the input and the LP and Learning Methodology used for it.
-Some LP engines are rule based (such as math or logic).
-Some LP engines are data based, e.g. ”poetry”.
-Data-based engines can be based on current Neural Networks, hardware accelerated networks, or other base technologies (quantum, biological computing).
-Content Classification engine is an instance of Conceptualization Systems.
KAG Squiglies are used to denote KAGs in the illustrations:

Component interactions with Knowledge Graphs
Events between a Learning Process (LP), the repository and other LPs are based on passing Knowledge Graphs (KGs).
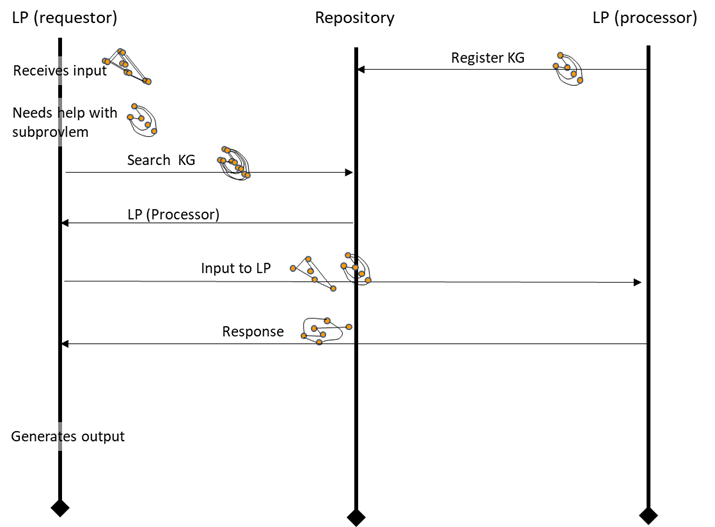
Event types:
-LP registers a set of keys with the repo. These keys describe the capabilities of the LP.
-A search by an LP (requestor) to the repo. Search term is one or more KGs.
-Response to the search by the repo. The response is zero or more LPs and their corresponding KG sets.
-LP triggers one or more other LPs(processor) with an Input. The input is passed as a KG.
-Response by the LP(processor) to the LP(requestor). Response is passed as a KG. Any activity by the LP can change its internal NN structures and content (learning).
The illustration shows only one requestor and processor for the sake of clarity.